Contents:
- Data Types in Java
- Primitive Types and Values
- Non-Primitive Types
- Difference Between Primitive Data Types and Non-Primitive Data Types
Data Types in Java
- Data type defines how much memory space represented by a variable need to be allocated and what kind of data a variable of that type will hold.
- There are two kinds of data types in Java: Primitive types and Non-Primitive Types(also called Reference type).
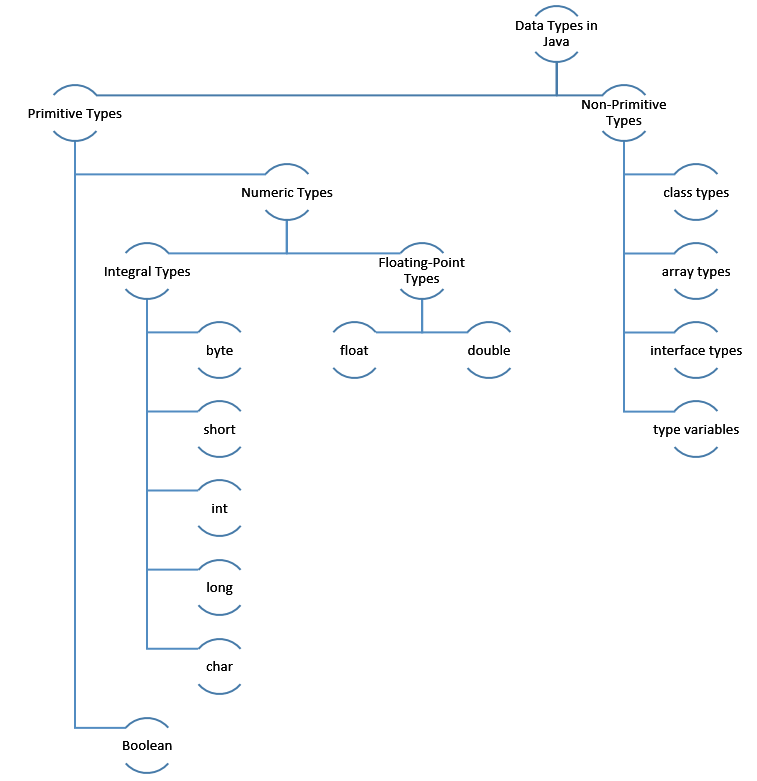
- So, there are two kinds of values that can be stored in a variable, passed as arguments and returned by methods depending on its type: primitive values and reference values.
- The primitive types represent single values, not complex objects.
Primitive Types and Values
- Java primitive types are also referred to as simple types which are already pre-defined in Java.
- Java defines total eight primitive types of data: byte, short, int, long, float, double, char, and boolean.
- The byte, short, int, and long data types come under integral type whose values are 8-bit, 16-bit, 32-bit and 64-bit signed integer numbers respectively.
- It means, they allow a variable to store either positive or negative integer numbers based on their sizes.
- In Java, to store characters in computer memory, we need char data type.
- It is important to understand that Java uses Unicode (an international character encoding standard that provides a unique number for every character across languages) to represent the characters and that is the reason char data types also comes under integral type but it allows a variable to store only 16-bit unsigned integer numbers.
- The size of integral primitive data types defines the range of integer values, a variable can hold.
- The values of the integral types are integers in the following ranges:
- For byte(size: 1 byte or 8 bits), from -128 to 127, inclusive
- For short(size: 2 bytes or 16 bits), from -32768 to 32767, inclusive
- For int(size: 4 bytes or 32 bits), from -2147483648 to 2147483647, inclusive
- For long(size: 8 bytes or 64 bits), from -9223372036854775808 to 9223372036854775807, inclusive
- For char(size: 2 bytes or 16 bits), from ‘\u0000’ to ‘\uffff’ inclusive, that is, from 0 to 65535
- In Java, floating-point types represent numbers with fractional parts.
- There are two floating-point types: float and double.
- The float and double data types follow IEEE 754 standards to store fractional data in 32-bit and 64-bit respectively.
- The way computer stores integer value into computer memory is totally different than storing fractional value into computer memory.
- IEEE 754 includes not only positive or negative numbers that consist of sign and magnitude but also positive or negative zeros, positive or negative infinities and special Not-a-Number values (abbreviation NaN).
- A NaN value is used to represent the result of certain invalid operations such as dividing zero by zero.
- NaN constants of both float and double type are predefined as Float.NaN and Double.NaN.
- The boolean type has exactly two values: true and false.
Non-Primitive Types
- Non-Primitive data types, also called as Reference types, are user defined except String type.
- Non-Primitive data types are used to store multiple values in computer memory unlike primitive data types which help to store only single value in computer memory.
- Variables of Non-Primitive data types does not directly hold the data but hold memory address of the data where they have been stored.
- Example of Non-Primitive data types: class, array, String, interface etc.
Difference Between Primitive Data Types and Non-Primitive Data Types
| Primitive Data Types | Non-Primitive Data Types |
|---|---|
| Primitive data types are predefined in java. | Non-Primitive data types are user defined. |
| Primitive data types have fixed sizes. | Non-Primitive data types have variable sizes. |
| Primitive data types handle single valued data . | Non-Primitive data types handle complex multi valued data. |
| Primitive data types support basic operations directly. | Non-Primitive data types often use method calls for operations. |